Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Cs in Cs adsorbent by LA-ICP-MS
Cs in Cs adsorbent by LA-ICP-MSAsai, Shiho*; Ohata, Masaki*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Yomogida, Takumi; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
A large amount of Cs adsorbents left over after decontamination of waste water has continued to accumulate in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. For safe disposal of such Cs adsorbents, estimation of the radioactivity is crucial. A long-lived beta emitting nuclide  Cs which is captured in the Cs adsorbents along with a major radiation contributor
Cs which is captured in the Cs adsorbents along with a major radiation contributor  Cs. Different from
Cs. Different from  Cs which can be measured in gamma spectrometry, the activity of
Cs which can be measured in gamma spectrometry, the activity of  Cs is generally measured in liquid form, requiring elution of Cs
Cs is generally measured in liquid form, requiring elution of Cs . However, high radiation from the Cs adsorbents hampers the operations. In this study, we applied LA-ICP-MS which allows direct measurement of Cs adsorbent. With
. However, high radiation from the Cs adsorbents hampers the operations. In this study, we applied LA-ICP-MS which allows direct measurement of Cs adsorbent. With  Cs /
Cs / Cs given by LA-ICP-MS,
Cs given by LA-ICP-MS,  Cs can be calculated by combining a measured
Cs can be calculated by combining a measured  Cs radioactivity. A radiocesium-containing sample was used to verify the proposed method. The results agreed well with those obtained through the measurement of Cs-separated solution.
Cs radioactivity. A radiocesium-containing sample was used to verify the proposed method. The results agreed well with those obtained through the measurement of Cs-separated solution.
 Sr in bones for ICP-MS analysis
Sr in bones for ICP-MS analysisKoarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kitamura, Akihiro
no journal, ,
Strontium-90 ( Sr) is one of an artificial radionuclide after the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. The ICP-MS system for
Sr) is one of an artificial radionuclide after the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. The ICP-MS system for  Sr have been developed. The ICP-MS system could apply to measurement of
Sr have been developed. The ICP-MS system could apply to measurement of  Sr in soils and water. In this study, solid phase extraction method of
Sr in soils and water. In this study, solid phase extraction method of  Sr was optimized the ICP-MS system for bones. After MW digestion, fish bone was dissolved in 2.6 M nitric acid. Sr resin was used for solid phase extraction of
Sr was optimized the ICP-MS system for bones. After MW digestion, fish bone was dissolved in 2.6 M nitric acid. Sr resin was used for solid phase extraction of  Sr in a flow-injection system. Sr and interference elements were determined with ICP-MS. Chemical yield of Sr was over 90% in the solid phase extraction system. Interference elements were removed in the extraction. The extraction method could applied to the ICP-MS system for
Sr in a flow-injection system. Sr and interference elements were determined with ICP-MS. Chemical yield of Sr was over 90% in the solid phase extraction system. Interference elements were removed in the extraction. The extraction method could applied to the ICP-MS system for  Sr. The method required only 30 minutes. The ICP-MS system would be rapid method for
Sr. The method required only 30 minutes. The ICP-MS system would be rapid method for  Sr measurement in bones.
Sr measurement in bones.
Matsueda, Makoto; Koarai, Kazuma; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kitamura, Akihiro
no journal, ,
Sr-90 accumulates in hard tissues such as bones and teeth in the case of uptake into the human or animal bodies. Therefore, the analysis of these hard tissues from the viewpoint of exposure evaluation has required, but the conventional radioactivity analysis requires a period of about one month, it is difficult to process a large number of samples. From this thing, we tried to apply application of the online solid phase extraction/ICP-MS method which can be measured quickly compared to radioactivity analysis. This method has mainly been utilizing as the analysis of Sr-90 contained in the water samples such as rainwater, and it has already equipped the correction functions corresponding to the shift of recovery rate at the Sr resin and the sensitivity shift in ICP-MS. However, hard tissues contain a large amount of matrix. Therefore, we investigated whether the isobaric interference, stable Sr, and other high matrix influence to Sr-90 values and attempted to correct the values.
Yomogida, Takumi; Esaka, Fumitaka; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Miyamoto, Yutaka
no journal, ,
Recently, we are applying micro-Raman spectroscopy (MRS) to the identification of the chemical states of uranium particles in environmental samples. Raman scattering intensity and spatial resolution increase with shortening laser wavelength. However, fluorescence from samples would be interferences in Raman analysis. It is important for Raman analysis to select the suitable laser wavelength. In this study, Raman spectra of uranium oxide particles were measured with two lasers: 532 nm laser and 785 nm laser. UO , U
, U O
O , and UO
, and UO n(H
n(H O) particles were used as samples. No fluorescence was observed in the Raman spectra of the uranium oxide particles. The characteristic Raman bands which derive from UO
O) particles were used as samples. No fluorescence was observed in the Raman spectra of the uranium oxide particles. The characteristic Raman bands which derive from UO , U
, U O
O , and UO
, and UO n(H
n(H O) were observed. As a result, 532 nm laser is suitable for Raman analysis of the uranium oxide particles in terms of sensitivity and spatial resolution.
O) were observed. As a result, 532 nm laser is suitable for Raman analysis of the uranium oxide particles in terms of sensitivity and spatial resolution.
Esaka, Fumitaka
no journal, ,
In order to detect the particles containing nuclear materials in the environment, we have developed a fission track (FT) technique. The positions of each particle containing nuclear materials can be identified by observing fission tracks created by neutron irradiation. Isotope ratios of nuclear materials in bulk samples are usually determined using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) or thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS). On the other hand, secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) is utilized for measuring isotope ratios in individual particles. In particular, large geometry-SIMS (LG-SIMS) having high transmission and mass resolution capabilities enables us to perform precise isotope ratio analysis. In this presentation, analytical techniques of individual particles using ICP-MS and TIMS as well as SIMS are presented.
Okamura, Hiroyuki; Ueda, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Mu, J.*; Masters, A. J.*; Antonio, M. R.*
no journal, ,
Recently, cluster formation of metal-extractant complexes in organic solvents has been shown to play important roles in liquid-liquid extraction. Although a number of reaction mechanisms have been proposed for liquid-liquid extraction, application of slope analysis method for evaluating metal-extractant stoichiometry fails when the solute concentrations are high. In this study, we performed the analysis of solvent extraction equilibria for practical liquid-liquid systems with consideration of the formation of cluster aggregates in the organic phase during the extraction process. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation indicates the formation of aggregated clusters of 1 to 9 Zr(NO )
) (TBP)
(TBP) complexes in
complexes in  -octane, leading to the determination of composition and molar fraction of each cluster. Furthermore, the extraction equilibrium reactions were studied, and the extraction equilibrium constant K
-octane, leading to the determination of composition and molar fraction of each cluster. Furthermore, the extraction equilibrium reactions were studied, and the extraction equilibrium constant K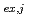 (
( = 1-9) for each cluster could be determined from the parameters obtained by the MD analysis. The distribution curve calculated from K
= 1-9) for each cluster could be determined from the parameters obtained by the MD analysis. The distribution curve calculated from K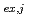 agrees well with the experimental values. Therefore, one MD simulation can accurately reproduce the distribution curve in the clustering/aggregation liquid-liquid extraction system, which enabled us to overcome the limitations of slope analysis method.
agrees well with the experimental values. Therefore, one MD simulation can accurately reproduce the distribution curve in the clustering/aggregation liquid-liquid extraction system, which enabled us to overcome the limitations of slope analysis method.
Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Koarai, Kazuma; Mitsuyasu, Yusuke*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sekine, Tsutomu*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; Chiba, Mirei*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; Osaka, Ken*; et al.
no journal, ,
Due to the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, the exposure dose estimation for human is examined by the whole body counter or by the Fukushima Health Management Survey, however, the precise estimated dose cannot obtained by such methods. We applied electron spin resonance (ESR) dosimetry for the external dose estimation using tooth enamel of human/animal. As we reported last year, we improved the detection limit of ESR dosimetry down to 43 mGy. We used this improved ESR dosimetry system and attempted to estimate the external dose of wild Japanese macaque capture in Fukushima prefecture, however, the metal component which may obstruct the ESR measurement was observed, so that we cannot estimate the external dose. In this work, we investigated how to remove such metal components, obtain the clear ESR spectrum, and estimate the external dose.
Eguchi, Ayano; Okamura, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Ueda, Yuki; Morita, Kotaro*; Shimojo, Kojiro; Naganawa, Hirochika; Hirayama, Naoki*
no journal, ,
Physical and chemical properties of ionic liquids (ILs) can be tuned by changing the combination of an anion and a cation composing an IL. In the solvent extraction of metal ions, it is considered that IL anions affect extraction by the interaction IL anions and metal ions. However, the structural effect of the IL anions on extraction is hardly clarified. In this study, the effect of the side chain of the IL anions on the IL chelate extraction of trivalent lanthanoids using 2-thenoyltrifluoroacetone was investigated. Four 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(perfluoroalkanesulfonyl)imides with different carbon number of side chain n (n = 1-4) were synthesized and used as extraction solvents. When n was even, the extracted species were different from those when n was odd. This result was considered to be due to the different IL solvation effects on the extracted complexes depending on n. It was implied that the side chain in the IL anions was involved in the extraction mechanism by affecting solvation of extracted complexes.